Best password managers are essential tools for safeguarding your online accounts. They offer a secure and convenient way to store and manage your passwords, protecting you from the risks of weak or reused passwords. This guide delves into the world of password management, exploring various options, security features, usability, and pricing models.
From simple browser extensions to robust standalone applications, we’ll examine the different types of password managers and their respective advantages. We’ll also compare their features, security protocols, and ease of use, empowering you to make informed decisions about which solution best suits your needs.
Introduction to Password Managers: Best Password Managers

Password managers are essential tools for securely storing and managing multiple online accounts. They simplify the process of creating and remembering strong, unique passwords for each site, significantly reducing the risk of account breaches. By automating password creation and storage, these programs protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.These programs provide a centralized platform to store and access passwords, eliminating the need to remember numerous complex credentials.
This simplifies the login process, preventing the use of weak or reused passwords, and enhancing overall online security.
Types of Password Managers
Password managers come in various forms, each catering to different user preferences and needs. Understanding these variations helps in choosing the most suitable solution.
- Browser extensions:
- These extensions integrate directly into web browsers, making password management seamless during online interactions. They typically operate within the browser environment, requiring no separate software installation. This approach is convenient for users who primarily access accounts through their browsers.
- Standalone applications:
- Standalone applications provide a more comprehensive suite of features, often extending beyond password management. They typically offer additional functionalities, such as secure note-taking, file encryption, and VPN services, catering to a broader range of security needs.
Popular Password Managers
Several popular password managers are available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right one depends on individual needs and priorities.
- 1Password:
- A popular choice known for its robust features and user-friendly interface. It offers strong encryption, customizable vault options, and various security enhancements. Its comprehensive features make it a favorite among users who need extensive security and organization.
- LastPass:
- Another widely used password manager known for its ease of use and extensive feature set. It provides a simple and straightforward interface for managing passwords, making it accessible to a wide range of users. Its strong encryption and automatic password generation capabilities further enhance security.
- Dashlane:
- This password manager offers a blend of features and functionalities, combining ease of use with a robust security infrastructure. It provides a seamless user experience, allowing users to manage passwords across various platforms.
Comparison of Password Manager Types
The table below compares different password manager types based on ease of use, features, and pricing models.
| Type | Ease of Use | Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Browser Extensions | Generally high; seamless integration with browsers | Limited compared to standalone apps; typically focused on password management | Often free with optional premium features |
| Standalone Applications | Generally high, but may have a steeper learning curve | Comprehensive; often include additional security tools like VPNs and file encryption | Typically subscription-based, with various tiers and options |
Security Features of Password Managers
Password managers are crucial for online security, safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access. They employ robust security protocols, effectively mitigating risks associated with weak passwords and phishing attempts. Understanding these features is paramount for selecting a reliable password manager.Top-tier password managers implement advanced security measures to protect user data. These measures range from encryption methods to multi-factor authentication, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of stored credentials.
This comprehensive approach reduces the likelihood of data breaches and safeguards against unauthorized access.
Encryption Protocols
Password managers utilize strong encryption algorithms to protect stored passwords. These algorithms transform passwords into unreadable ciphertexts, rendering them inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. This process involves converting data into an unintelligible format using complex mathematical operations, making it virtually impossible to decipher without the appropriate decryption key. Common encryption methods include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and other industry-standard protocols.
For instance, 256-bit AES encryption is widely regarded as a strong standard for protecting sensitive data.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Implementing 2FA adds an extra layer of security to password managers. This method requires users to provide two distinct authentication factors—something they know (password) and something they have (e.g., a mobile device). This effectively mitigates the risk of unauthorized access even if an attacker compromises one factor. This crucial feature strengthens the overall security posture by demanding a combination of factors before granting access.
Protection Against Phishing and Malware
Password managers play a vital role in safeguarding against phishing attacks. They often incorporate mechanisms to detect suspicious links and websites, preventing users from entering credentials on fraudulent platforms. Furthermore, some password managers integrate malware protection to identify and block malicious software, preventing potential compromises of sensitive information. These features collectively contribute to a secure environment for users.
Factors Contributing to Password Manager Security
Several factors influence the security of password managers. These include the strength of the encryption algorithms, the reliability of the provider, and the security measures implemented to protect user data from breaches. The company’s track record, commitment to security audits, and transparent communication about security incidents are critical aspects. Furthermore, the password manager’s architecture and design significantly affect its overall security posture.
Solid password managers are crucial for online security, but knowing how to use Git effectively can also boost your digital safety. Learning the ropes of version control, as outlined in the GitHub beginner guide , can help you manage your sensitive information in a more organized and secure manner. Ultimately, a strong password manager and a grasp of Git principles work hand-in-hand for better digital hygiene.
Importance of Strong Passwords and Password Manager Assistance
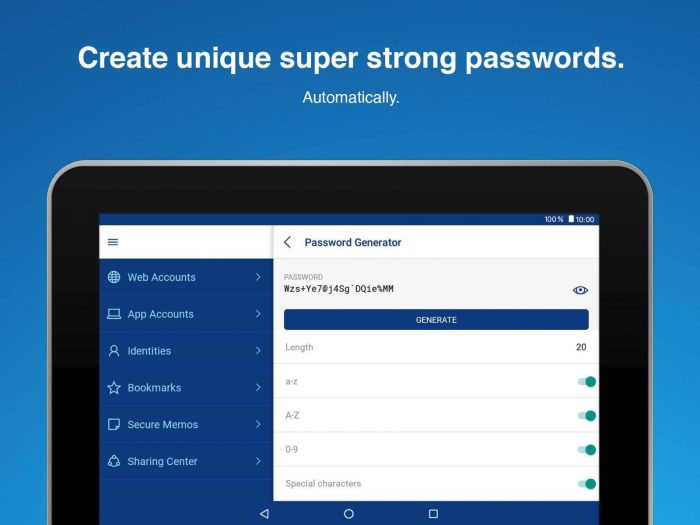
Strong passwords are essential for robust online security. Password managers significantly assist in generating and managing these strong passwords. They often include password generators that create complex and unique passwords, reducing the risk of brute-force attacks. This feature is invaluable, particularly for users managing numerous accounts with varied requirements. Furthermore, password managers help enforce password complexity standards, which are often required for account security.
Comparison of Password Manager Security Features
| Password Manager | Encryption | 2FA | Phishing Protection | Malware Protection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Password Manager A | AES-256 | Yes (SMS/Authenticator App) | Yes (URL filtering) | Yes (Real-time scanning) |
| Password Manager B | AES-256 | Yes (Authenticator App only) | Yes (Domain reputation) | Yes (Integration with antivirus) |
| Password Manager C | AES-128 | Yes (SMS/Authenticator App) | Yes (URL blacklisting) | No |
This table provides a basic comparison of security features across different password managers. Factors such as encryption strength, 2FA support, and protection against phishing and malware vary between providers. A comprehensive evaluation of security features should consider these factors in detail.
Usability and User Experience
Password managers are designed to streamline the complexities of managing numerous online accounts and passwords. A key aspect of their effectiveness lies in their user-friendliness and intuitive design. A seamless user experience ensures that users can easily navigate the platform, generate strong passwords, and securely store their sensitive information.A well-designed password manager should prioritize intuitive navigation and clear visual cues to guide users through the process.
This includes straightforward interfaces for adding accounts, generating passwords, and retrieving stored credentials. An effective user interface (UI) design should minimize the cognitive load on users, allowing them to focus on managing their passwords efficiently rather than wrestling with complicated features.
Ease of Use and Interface Design
Password managers vary significantly in their approach to user interfaces. Some opt for a minimalist design, prioritizing simplicity and clarity. Others incorporate more advanced features, which can sometimes lead to a more complex interface. A well-structured interface is crucial for user adoption. This allows users to easily locate necessary functions and add, manage, and retrieve accounts without undue difficulty.
Intuitive design elements, like clear labels, visual cues, and well-organized layouts, are vital to user satisfaction.
Password Generation and Management
The quality of password generation is a critical aspect of user experience. Password managers should offer options for generating strong, unique passwords. This can be achieved through the incorporation of diverse character sets and lengths. Robust password management tools should also support the safe storage and retrieval of these passwords. A user should be able to access and modify their stored information without any significant obstacles.
Simplification of Password Management Tasks
Password managers simplify password management tasks in several ways. They automate the process of creating and storing strong passwords, reducing the risk of weak or reused passwords. The centralized storage of credentials also streamlines the process of accessing different accounts. This streamlined access reduces the cognitive load associated with remembering numerous passwords, freeing up mental resources for other tasks.
Further, the automatic synchronization of data across devices enables seamless access to accounts from any location.
Comparison of User Experiences
| Password Manager | Interface Design | Password Generation | Account Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Password Manager A | Clean and minimalist, intuitive navigation. Focuses on clear visual cues. | Offers diverse character sets and customizable length options for strong password generation. | Easy to add, edit, and delete accounts. Supports account import/export. |
| Password Manager B | More complex interface, but offers a wide range of advanced features. Some find it overwhelming. | Includes sophisticated password generation options with customizable criteria. | Extensive features for managing various account types. Excellent security features. |
| Password Manager C | User-friendly interface, emphasizing simplicity. Easy to learn. | Provides good options for strong password generation. | Straightforward account management features, suitable for beginners. |
Features and Functionality
Password managers are more than just tools for storing passwords. They offer a suite of features designed to enhance online security and streamline digital life. Beyond basic password storage, they provide robust functionality for secure note-taking, file encryption, and integration with various applications. This section explores the diverse capabilities of password managers and how they can be applied across personal and professional contexts.Password managers are evolving beyond their core function of password storage.
They are becoming essential tools for managing sensitive information, streamlining digital workflows, and improving overall online security. Understanding the breadth of their features is crucial for appreciating their potential and choosing the right solution for individual needs.
Different Features Offered
Password managers provide a range of features beyond simply storing passwords. These features enhance security and convenience, making them more than just password vaults. They often include secure note-taking capabilities, allowing users to store sensitive information like personal details, travel itineraries, or financial records. These notes are often encrypted, adding an extra layer of security. File encryption is another common feature, enabling users to protect documents and files stored within the password manager’s ecosystem.
This ensures that sensitive data is protected even if the password manager itself is compromised.
Examples of Use Cases
Password managers are applicable across a wide spectrum of activities. For personal use, they can manage login credentials for email accounts, social media platforms, and online banking portals. They are also valuable for managing various subscriptions and memberships. Professionally, password managers can help manage access to company systems, customer data, and other sensitive information. They can even be used for project management, securely storing documents and project-related details.
The versatility of password managers is demonstrated by their diverse applications.
Common Features Categorized
Password managers typically offer a range of features, which can be categorized for clarity. This structured approach helps users understand the full scope of functionality.
- Password Management: Core function of storing and managing user passwords, often with strong password generation capabilities and automatic filling for various websites.
- Secure Note-Taking: Allows users to store and encrypt notes, documents, and sensitive information, protecting it from unauthorized access. This often includes tagging and organization features for efficient retrieval.
- File Encryption: Enables users to encrypt and securely store files within the password manager’s environment, adding an extra layer of protection for sensitive documents and data.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) Support: Integrating with 2FA providers, allowing for seamless and secure login processes.
- Data Backup and Synchronization: Critical features for ensuring data safety and accessibility across multiple devices. The ability to sync data between devices ensures seamless access from any location.
- Integration with Other Applications: Facilitates the seamless integration of password managers with other software and platforms, improving workflow efficiency and security.
Password Syncing and Data Backups
Data syncing and backups are critical for password managers. They ensure that user data is accessible across various devices and that it’s protected from potential loss or damage. A well-implemented system allows users to access their information on any device with an active internet connection. Reliable backup procedures provide a safeguard against data loss due to device failure or other unforeseen circumstances.
Data backup and synchronization are crucial for maintaining the integrity and accessibility of sensitive information managed by password managers.
Integration with Other Applications, Best password managers
Integration with other applications is a key aspect of password managers. It allows for seamless data transfer and automated actions, enhancing productivity and security. Integration with email clients, project management tools, and other software allows for streamlined workflows. For example, automatic filling of login credentials when accessing various applications reduces the need for manual input, saving time and minimizing the risk of errors.
Cost and Pricing Models
Password managers offer a range of pricing models, catering to various budgets and needs. Understanding these models is crucial for selecting the right solution for your security and convenience requirements. A well-chosen password manager can significantly improve your online security posture.The pricing models vary widely, from entirely free options with limited features to premium services with advanced functionalities.
The value proposition of each tier is directly correlated with the features offered. Free versions often serve as a good introduction to password management, allowing users to experience the benefits before committing to a paid subscription.
Pricing Tier Comparisons
Different password managers employ various pricing models. Free tiers often include essential features like password generation and storage, but with restrictions on storage capacity and/or features. Paid tiers generally unlock more comprehensive functionalities, including enhanced security measures, increased storage, and specialized features.
Free Tier Features
Free tiers typically provide a taste of the password management experience. Essential functions like password generation and storage are usually included, allowing users to appreciate the benefits of centralized password management. However, features like unlimited storage, advanced security features, and customer support may be limited.
Paid Tier Features
Paid tiers offer enhanced functionality, expanding the capabilities of password managers. Unlimited storage, advanced security features, two-factor authentication, and dedicated customer support are often included in these tiers. Furthermore, access to additional features like data backup and recovery, and potentially even enhanced security auditing, are more likely to be part of a paid tier.
Comparison Table of Pricing Models
| Password Manager | Free Tier | Paid Tier | Value Proposition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Password Manager A | Basic password generation, storage for a limited number of items, basic syncing | Unlimited storage, advanced security features (e.g., two-factor authentication), customer support, device management | Provides a user-friendly interface for managing passwords, with more advanced security features available in the paid version. |
| Password Manager B | Limited number of password storage slots, basic syncing across devices | Unlimited storage, advanced security features, unlimited device management, backup and recovery, multi-factor authentication | Offers comprehensive security features and seamless integration across various devices in the paid tier. |
| Password Manager C | Limited number of passwords, limited storage, limited device syncing | Unlimited storage, advanced security features, unlimited device management, customer support, advanced data security audit tools | Provides comprehensive security and user-friendly features, especially in the premium subscription. |
Pricing Tier Feature Summary
This table summarizes the features of different pricing tiers for various password managers, highlighting the key differences and value propositions.
| Password Manager | Free Tier Features | Paid Tier Features |
|---|---|---|
| Password Manager A | Basic password generation, storage, syncing | Unlimited storage, advanced security features, 24/7 customer support |
| Password Manager B | Limited passwords, basic syncing | Unlimited storage, advanced security features, device management, backup and recovery |
| Password Manager C | Limited password storage, basic syncing | Unlimited storage, advanced security, data backup, security audit tools, 2FA |
Integration with Other Applications
Password managers aren’t isolated tools; their effectiveness hinges on seamless integration with other applications. This integration streamlines workflows, enhances security, and elevates the user experience. By working harmoniously with browsers, operating systems, and productivity tools, password managers empower users to manage their digital lives more efficiently and securely.Integrating password managers with other applications is crucial for a unified and streamlined security approach.
A password manager that can effortlessly share and utilize credentials across different applications is a powerful tool for improved productivity and peace of mind. This interconnectedness facilitates efficient and secure access to various digital services.
Browser Integration
Password managers seamlessly integrate with web browsers, storing and auto-filling credentials. This eliminates the need to manually type passwords, enhancing convenience and security. The automatic filling feature significantly reduces the risk of typing errors or using weak passwords. Password managers often have extensions for popular browsers, ensuring a smooth and integrated user experience. Many password managers allow users to import and export their browser passwords, facilitating a transition between different browsers or systems.
Operating System Integration
Modern password managers frequently integrate with operating systems, providing an overarching security solution. This integration extends beyond password management to encompass broader security features, such as two-factor authentication or device encryption. The seamless integration with the operating system provides a unified interface for managing various security aspects. Some operating systems even offer native support for password managers, enhancing security and convenience.
Integration with Productivity Tools
Password managers can integrate with productivity tools like project management software, email clients, and note-taking apps. This integration often allows for the automatic filling of credentials in these tools, improving the efficiency of workflow. For instance, a password manager might automatically fill in login credentials for a project management platform when required, allowing users to focus on tasks rather than login details.
The integration with productivity tools empowers users to effortlessly access various accounts and manage projects securely.
Integration with Email Clients
Integrating password managers with email clients provides enhanced security. This integration facilitates the secure storage and auto-filling of credentials for email accounts. This can further reduce the risk of phishing attacks and compromised accounts. By using a password manager for email, users can avoid the need to type sensitive information repeatedly, minimizing potential errors and increasing security.
Furthermore, the secure storage of email passwords within a password manager enhances overall security posture.
Overview of Platform Integration
Password managers support a variety of platforms, including Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android. The compatibility extends to a wide range of web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. This broad platform support ensures users can maintain a consistent security posture across different devices and applications. This flexibility allows users to seamlessly manage their passwords and access various online services regardless of the platform or device they are using.
Cross-platform compatibility is crucial for users who need to access their accounts and manage their security from multiple devices.
Strong password managers are crucial for online security, and a robust system is key. Choosing the right one can be tricky, but a good password manager can significantly improve your digital safety. Considering the delicate craftsmanship of a cushion cut with halo setting, cushion cut with halo setting jewelry, for instance, highlights the meticulous detail and precision that’s essential in selecting the best password managers.
Ultimately, a secure password manager is a worthwhile investment for anyone managing online accounts.
Customer Support and Help Resources
Password managers, while offering robust security, rely on effective customer support to address user queries and resolve issues. A well-maintained support system is crucial for user satisfaction and trust in the platform. This section delves into the various support methods offered by popular password managers, assessing their accessibility and effectiveness.
Different Support Options
Password managers provide a range of support channels to address user needs. These options typically include frequently asked questions (FAQs), email support, and live chat. Understanding the availability and quality of these options is critical when evaluating a password manager.
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): A comprehensive FAQ section can answer many common user queries without requiring direct interaction with support staff. Well-organized FAQs provide quick answers to common issues, saving both the user and the support team time. This approach allows users to troubleshoot problems independently and efficiently.
- Email Support: Email support provides a more formal channel for detailed inquiries and complex problems. The responsiveness and helpfulness of the email support team are crucial for user experience. Users expect a timely and informative response to their email queries.
- Live Chat: Live chat offers immediate assistance, enabling users to receive instant support for issues requiring immediate attention. This real-time interaction is particularly beneficial for resolving urgent problems or for users seeking clarification on complex functionalities.
Accessibility and Effectiveness of Support Methods
The effectiveness of a support system is judged by its accessibility and the quality of the responses. A user-friendly interface for accessing FAQs and a quick response time for email and live chat are important factors.
- FAQ Accessibility: The organization and clarity of FAQs are crucial. Poorly structured FAQs can make finding answers difficult, leading to frustration. A well-organized, searchable FAQ section significantly improves the user experience.
- Email Response Time: A quick response time for email support is essential. Unnecessarily long wait times can deter users from seeking help and lead to dissatisfaction. Password managers with consistently fast email responses build user trust and demonstrate commitment to customer service.
- Live Chat Availability: The availability of live chat support varies across password managers. Consistent availability, especially during peak hours, is crucial for users needing immediate assistance. The availability of live chat during off-peak hours can also be a deciding factor.
Importance of Readily Available Support
Robust customer support is vital for building trust and ensuring user satisfaction. Users often rely on password managers to safeguard sensitive information, and a strong support system provides confidence and reassurance. Reliable support ensures that users can effectively use the password manager’s features and quickly resolve any issues that may arise.
Examples of Customer Support Experiences
While specific examples of customer support experiences are often proprietary, general observations can be made. Some password managers are known for their proactive and helpful support teams, while others may have a reputation for slower responses or less comprehensive support. The quality of customer support is a key differentiator among password managers.
Comparison of Support Options
| Password Manager | FAQ Accessibility | Email Response Time | Live Chat Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Password Manager A | Good, searchable, well-organized | Fast, usually within 24 hours | Available during business hours |
| Password Manager B | Fair, but could be more intuitive | Moderate, usually within 48 hours | Limited availability |
| Password Manager C | Excellent, comprehensive | Very fast, often within hours | Available 24/7 |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison. Specific experiences may vary.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, choosing the right password manager is crucial for online security. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the various options available, helping you evaluate features, security, usability, and pricing. By carefully considering your needs and preferences, you can select a password manager that effectively protects your sensitive information and simplifies your online experience.
Question Bank
What are the common security protocols used by password managers?
Many password managers employ robust encryption protocols, like AES-256, to protect your data. Two-factor authentication (2FA) is also a common feature to add an extra layer of security. Other security features include strong password generation tools and protection against phishing attempts.
How do password managers help protect against phishing and malware?
Password managers can help protect against phishing attacks by warning you about suspicious websites and preventing you from entering your credentials on fake login pages. Some password managers also include features that can detect and block malicious websites, reducing your exposure to malware and other threats.
What are some of the different types of password managers available?
Password managers come in various forms, including browser extensions, standalone applications, and even features built into some operating systems. Each type has its own set of pros and cons, so it’s important to consider what works best for your needs.
What is the importance of strong passwords and how do password managers assist in creating them?
Strong passwords are crucial for online security. Password managers often have built-in tools that generate strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts. They also help you avoid reusing passwords, significantly enhancing your overall online security.